Project
Good News for Vietnam Rubber Group (GVR): Approval Granted for Bac Dong Phu Industrial Park Phase 2
Published
1 year agoon
Deputy Prime Minister Tran Hong Ha signed Decision No. 145/QD-TTg on January 16, 2025, approving the investment policy for the construction and infrastructure business project of Bac Dong Phu Industrial Park Phase 2 in Binh Phuoc Province. The project investor is Bac Dong Phu Industrial Park JSC, a member of Vietnam Rubber Group (stock code GVR).
The two major shareholders of Bac Dong Phu Industrial Park are Dong Phu Rubber JSC (stock code DPR) with a 51% ownership stake and Nam Tan Uyen Industrial Park JSC (stock code NTC) with a 40% ownership stake.
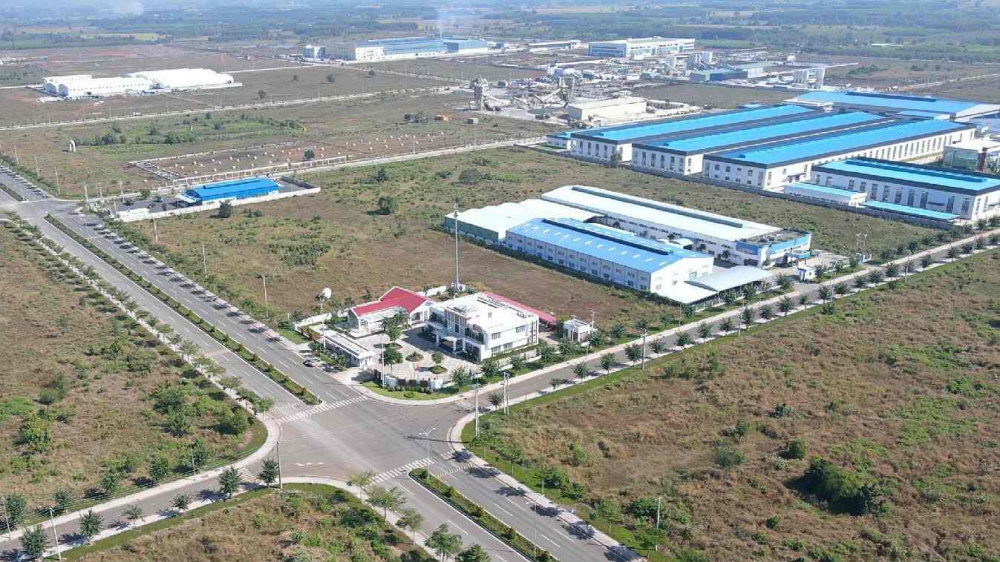

The industrial real estate sector is expected to become a new growth driver for Vietnam Rubber Group.
The Bac Dong Phu Industrial Park Phase 2 project will be developed in Tan Phu Town, Dong Phu District, and Tien Hung Commune, Dong Xoai City, Binh Phuoc Province, with a total land area of 317 hectares. The total investment for the project is VND 1,360 billion, including VND 204 billion in investor equity.
This is the second large-scale industrial park project approved for Vietnam Rubber Group in recent weeks. On December 27, 2024, the expansion of Rach Bap Industrial Park (360 hectares) in Binh Duong Province, led by An Dien Industry JSC (a subsidiary of Vietnam Rubber Group holding a 92.67% stake), was also approved for development.
Bac Dong Phu Industrial Park Phase 2 is a highly anticipated project for Vietnam Rubber Group, Dong Phu Rubber, and Nam Tan Uyen Industrial Park amidst the limited availability of commercial industrial land within their portfolios.
One of the bottlenecks delaying the approval of Bac Dong Phu Industrial Park Phase 2 was the near-exceedance of Binh Phuoc Province’s allocated industrial land quota, as stipulated in Decision No. 326/QD-TTg issued on March 9, 2022, by the Prime Minister. This decision set national land use allocation targets for the 2021–2030 period, with a vision to 2050, and a five-year land use plan for 2021–2025.
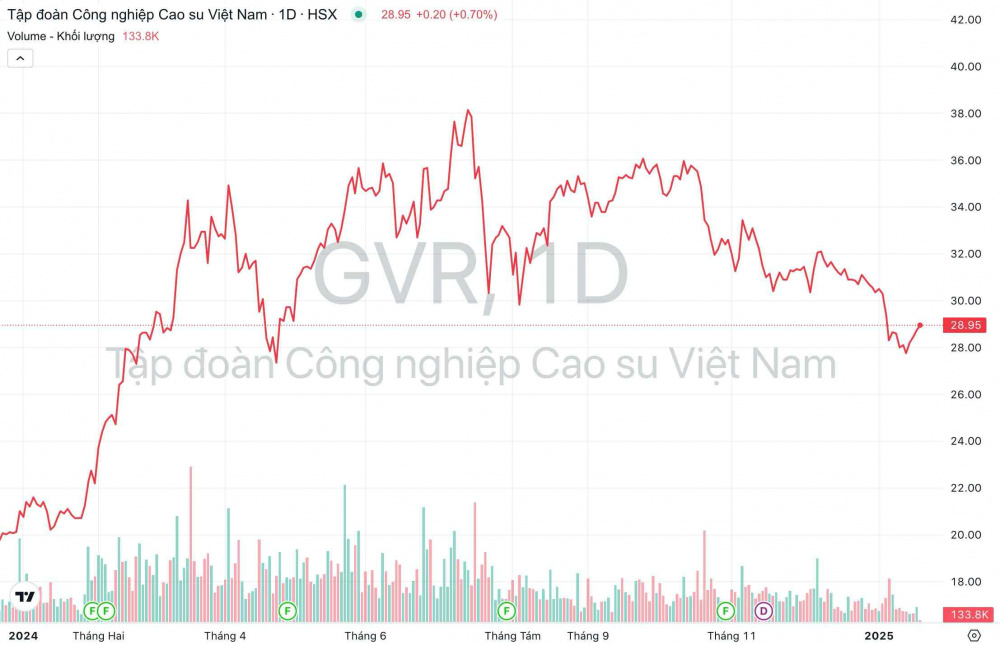
The price movements and trading volume of Vietnam Rubber Group’s GVR stock from the beginning of 2024 to now. (Source: TradingView)
However, in March 2024, the Prime Minister issued Decision No. 227/QD-TTg, adjusting some land use targets until 2025, as allocated in Decision No. 326/QD-TTg. Consequently, Binh Phuoc Province gained an additional 828 hectares of industrial land for new projects by 2025, including Bac Dong Phu Industrial Park Phase 2.
With 317 hectares of industrial land added to the portfolio, Bac Dong Phu Industrial Park Phase 2 is expected to drive new growth for Dong Phu Rubber and Vietnam Rubber Group.
In terms of business performance, Vietnam Rubber Group estimated its consolidated revenue for 2024 to reach VND 26,307 billion, achieving 105.2% of the annual target and up 6.5% compared to 2023. Consolidated after-tax profit is projected to be VND 3,746 billion, reaching 109% of the annual target and increasing by 11% compared to 2023.

You may like
Project
Vietnam’s Exclusive Economic Zone boasts over 1,000 GW of wind power potential: report
Published
11 months agoon
April 27, 2025Vietnam’s Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) has a wind power potential of 1,068 GW, nearly 470 GW more than previously estimated, according to a report released Friday by the National Center for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasting (NCHMF).

An offshore wind power project in Vietnam. Photo courtesy of VnEconomy.
The report, titled “Detailed Assessment of Wind Resource Potential in Coastal (up to 6 Nautical Miles) and Offshore Areas in Vietnam,” was conducted by the NCHMF with support from the United Nations Development Program (UNDP) and the Norwegian Embassy.
This wind potential was measured at a height of 100 meters above sea level, said Mai Van Khiem, director of the NCHMF. He noted that from November to February each year, wind capacity accounts for half of the annual total – peaking in December and gradually decreasing, with the lowest levels recorded in May.
The southern offshore areas account for 894 GW of this potential, while the northern areas contribute 174 GW.
In nearshore zones (up to 6 nautical miles), the total technical wind power potential is 57.8 GW. The Bac Lieu-Ca Mau region alone contributes nearly 30% of this, while the Ninh Thuan-Binh Thuan area accounts for 24 GW. Although the Quang Tri-Hue region has lower potential, it offers stable wind speeds during the winter months. The Red River Delta has a modest potential of 0.17 GW.
Compared to previous assessments, such as the World Bank’s 2021 study and data from the Global Wind Atlas (GWA), this report provides more detailed and higher-resolution information, both spatially and temporally.
“Notably, the EEZ potential outlined in this report exceeds the World Bank’s estimate by 469 GW, primarily due to the broader scope of the survey and more refined climate modeling using domestic observational data,” the research team explained.
They also emphasized the use of the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model customized specifically for Vietnam, which enhanced the accuracy of the results.
The findings are based on wind data collected from 26 coastal and island meteorological stations, satellite sources from CCMP, ASCAT, and SCATSAT-1 (covering 30 years of ocean surface wind data), as well as buoy data from Nghe An province and seabed depth measurements.
A key innovation in this report is the integration of potential impacts from extreme weather events. Typhoons and tropical depressions occurring between August and October pose structural and safety risks to wind turbines. Meanwhile, strong winds and high waves during the northeast monsoon season can hinder access to and maintenance of offshore wind systems.
To support model calibration and long-term observation, the research team recommends increased investment in offshore wind monitoring stations at heights exceeding 100 meters. They also suggest incorporating these findings into offshore wind development strategies and national marine spatial planning.
Additionally, the team advocates for expanding research into other forms of marine renewable energy, such as wave, tidal, and ocean thermal energy.
“Vietnam has some of the most promising offshore wind resources in the region, creating a strong foundation for the development of a large-scale offshore wind industry. This will contribute to energy security, green economic growth, and the achievement of net zero commitments,” they said.
The study provides a vital scientific basis for policy planning, identifying priority development zones, attracting investment, building infrastructure, and training the future offshore wind workforce, the team added.
Hoang Duc Cuong, deputy director of the Department of Meteorology and Hydrology, emphasized that Vietnam lies within a strong and stable Asian monsoon belt, giving it abundant wind energy potential. He noted that this renewable source will play a key role in meeting the country’s climate change goals and advancing a low-carbon economy.
However, he also warned that marine-based natural disasters are highly complex and could significantly impact the stability of offshore wind operations and energy generation.
The ever-changing status of the global economy following last week’s tariff shocks continue to loom large among investors in Vietnam’s real estate market.
 |
| All real estate segments are at risk of losing appeal if high global tariffs are eventually put in place, photo Le Toan |
Pham Lam, vice chairman of the Vietnam Real Estate Association, said that while it is premature to determine the full impact of new US import tariffs on Vietnam’s property market, early signs point to shaken investor sentiment and potential disruptions to foreign investment.
“If multinational corporations scale back or delay their factory expansion plans, the demand for land and factory leasing could decline, which may place downward pressure on industrial rents, lead to increased vacancy, and postpone new industrial zone developments,” he said. “This would affect key industrial property markets such as Bac Ninh, Bac Giang, Haiphong, Long An, and Binh Duong.”
Meanwhile, real estate expert Nguyen Hoang said that the United States remains one of the most critical export destinations for Vietnam’s foreign-invested enterprises.
“Any change in tariffs will significantly influence capital flows, investor confidence, and manufacturing strategies of companies operating in Vietnam. If a high tariff is fully implemented in 90 days, it could seriously diminish Vietnam’s investment appeal – affecting all real estate segments as a result,” Hoang said.
Vietnam’s property market has only recently emerged from a prolonged two-year downturn.
“It remains highly sensitive to economic and policy shocks. Investors have remained cautious, and any further external pressure could threaten to break the fragile liquidity recovery, potentially sending the market back into a period of short-term stagnation,” Hoang added.
Alex Crane, managing director of Knight Frank Vietnam, said that the recent tariff twists by the US casts a shadow of uncertainty, with potential implications for various segments of the market.
While manufacturing has shown resilience, it is still on the path to full recovery from the pandemic, particularly in labour-intensive sectors like garments and furniture. Tariffs imposed now would not have as severe an impact as they might have during Vietnam’s 2019 peak, but consequences are still expected, Crane said.
“I may expect that major transactions, especially those involving large capital outlays, are being paused or undergoing extended due diligence as investors and developers reassess assumptions and underwriting models and commercial occupiers are expected to defer large capital expenditures in the short term,” Crane said.
In addition, the response from the State Bank of Vietnam, particularly regarding monetary policy, will be crucial. While a rate cut may not effectively stimulate residential demand (as demonstrated in 2024), targeted lending for key industries and easing of loan-to-value ratios or debt-to-income limits for developers could provide relief.
“At present, most segments of the real estate market are in a holding pattern, awaiting clarity from the evolving negotiations between the Vietnamese and US governments. While uncertainty is unsettling, Vietnam’s underlying fundamentals remain sound, and the market’s long-term outlook is still viewed positively,” he added.
Nguyen Dung Minh, deputy CEO of MIK Group, has warned that under the new US tariff regime, many investors will be forced to reassess their strategies, likely leading to a decline in the demand for industrial land.
“Investors will need time to re-evaluate their actual demand and incoming orders and make necessary adjustments before they can fully gauge the extent of the impact,” Minh said.
He added that the implications go beyond just industrial land. “The new US tariffs are also expected to disrupt supply chains and negatively affect supporting sectors such as logistics, warehousing, and raw materials manufacturing. As production slows, so too will the demand for land associated with these services,” Minh said.
| Trang Bui, country head Cushman & Wakefield Vietnam
While the effects of tariffs are typically delayed, most economists warn that they may eventually fuel inflation and dampen economic growth. Many manufacturing firms could opt to postpone their expansion plans in the short term if export duties become too burdensome. There is also a possibility that some companies may look to diversify their supply chains towards a Vietnam+1 model, shifting parts of their operations to neighbouring countries. This could lead to a decline in demand for factories and warehouse leasing, two key drivers of the industrial real estate segment. However, it is important to recognise that industrial real estate is fundamentally a long-term investment. Vietnam has long positioned itself as the manufacturing hub of Southeast Asia, thanks to its strategic location and the “bamboo diplomacy” approach, which has enabled the country to swiftly join trade negotiations and sign multiple free trade agreements. Moreover, many manufacturers in Vietnam have already established tightly integrated supply chains. As such, their investment plans tend to operate on a much longer time horizon than the near-term effects of tariff policy. Relocating supply chains typically requires at least 3–5 years, making short-term shifts less likely. Overall, Vietnam’s industrial real estate sector has proven resilient under various political and economic conditions. Investors would do well to focus on long-term trends and structural advantages. Manufacturers, in particular, may take this opportunity to secure high-quality industrial assets, invest in automation, and pull in skilled labour, while continuing to monitor developments in upcoming trade negotiations with caution. Nguyen Thi Bich Ngoc, CEO, Sen Vang Group When it comes to the reciprocal tariff policy announced by the US, the greater danger currently lies not in the tariff itself, but in the heightened sense of uncertainty it has triggered across the Vietnamese market, a sentiment clearly reflected in recent VN-Index fluctuations. In the short term, the policy will weigh heavily on Vietnam’s industrial real estate sector. However, in the long run, this challenge could serve as a catalyst for stronger growth. It presents an opportunity for the government and industrial zone developers to rethink their strategies, offering more competitive, attractive solutions to both foreign and domestic investors. Rather than relying solely on external trends like the China+1 shift, Vietnam should leverage its inherent competitive advantages, including a strategic geographic location, a skilled and cost-effective labour force, and political stability, to pull in long-term investment. These are undeniable strengths that set Vietnam apart. Moreover, this is also an opportune moment for Vietnam to re-evaluate and restructure its key sectors, prioritising strategic industries with high growth potential. Continued engagement in bilateral and multilateral trade agreements will open up new opportunities and elevate Vietnam’s position both regionally and globally. Ultimately, we must seize this challenge as a turning point, transforming pressure into momentum for sustainable development. Vo Hong Thang, Investment director DKRA Group The industrial infrastructure, commercial, and residential real estate segments are all likely to face increasing headwinds if a huge tariff increase is eventually implemented. In recent years, a number of developers have made significant investments in industrial zones, betting on a continued influx of foreign direct investment. However, the new tariff policy raises the possibility of such flows being diverted to other countries. Vietnam now faces the risk of having built the nest, but being unable to attract the eagle. In addition, liquidity in both residential and commercial real estate, including retail, office, and hospitality, is likely to weaken in the short term due to more cautious investor sentiment, defensive capital flows, and reduced purchasing power from end-users. Niche investment segments such as serviced apartments, tourism-related accommodations, and foreign buyer housing could also see demand drop, particularly as the foreign expert and executive workforce, typically a key demand driver, scales back plans to live and work in Vietnam. |
Project
Central Vietnam city seeks $1.84 bln for 15 projects in economic zone
Published
11 months agoon
April 26, 2025Authorities of Hue city in central Vietnam have released a list of 15 projects in Chan May-Lang Co Economic Zone which will need VND47.5 trillion ($1.84 billion) in investment capital between 2025 and 2026.
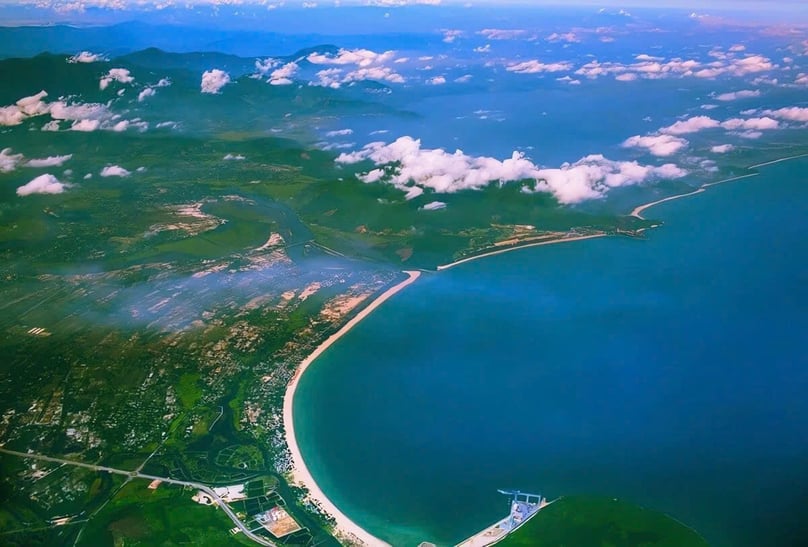

Chan May-Lang Co Economic Zone in Hue city, central Vietnam. Photo by The Investor/Dinh Duy.
Notable projects include the Chan May non-tariff zones No. 1 and 2 infrastructure development project, with a total area of over 503 hectares and combined investment capital of VND2.8 trillion ($108.23 million).
Another is the VND20 trillion ($773 million) Chan May Urban Area project (locations 1 and 2), which will cover 225 hectares and be implemented over five years.
The LNG terminal project at Chan May Port, 27 hectares with an investment of VND8.6 trillion ($332.43 million), is set for five-year implementation.
The 120-hectare Bai Ca eco-tourism project in Lang Co township will have investment capital of VND2.5 trillion.
The Lang Co beach resort, with an area of 45 hectares and total investment of VND4 trillion ($154.62 million), will be carried out over five years; while the 75-hectare Lap An lagoon tourism, urban development and resort complex in Lang Co township will cost VND6 trillion.
According to the management board of Hue Economic and Industrial Zones, since its establishment, Chan May-Lang Co Economic Zone has attracted 55 investment projects which remain valid, with total registered capital of VND97.32 trillion ($3.76 billion).
Among these, 15 are foreign-invested projects with combined capital of VND56.02 trillion ($2.17 billion), accounting for 57.56% of the total.
Several prominent foreign investors have established a presence in the zone, such as Banyan Tree Group (Singapore) with the Laguna Lang Co Resort and Winson Group (Taiwan) with the Billion Max Vietnam Export Processing Factory.
Chan May-Lang Co has become a destination for investments in sectors like tourism and resort development; seaport infrastructure; logistics; clean industry; and high-tech, environmentally friendly industries, with annual revenue reaching nearly VND4 trillion ($154.62 million) and tax contributions of around VND300 billion.
The management board said Hue city has proposed the Ministry of Construction review the adjustment of the EZ master plan through 2045, for submission to the Prime Minister.
The strategic goal is to develop Chan May-Lang Co into a key economic zone of central Vietnam – a coastal gateway offering logistics services for the central region and the East-West Economic Corridor, as well as a hub for high-end tourism services.
To attract investors, the local government will offer a range of incentives such as a 10% corporate income tax rate for 15 years from the first year the project generates revenue; import tax exemption for goods to create fixed assets for investment projects, and land and water surface rental exemptions, the board said.

Bac Giang International Logistics Centre launched

Vietnam’s Exclusive Economic Zone boasts over 1,000 GW of wind power potential: report

Uncertainty weighing on real estate

Central Vietnam city seeks $1.84 bln for 15 projects in economic zone
